1) Racism - a person who believes that a particular race is superior to another.
Suggestion to avoid racism
Avoid confirming and disconfirming to statement or message because of skin color.
2) Sexism - Having bias towards a specific gender.
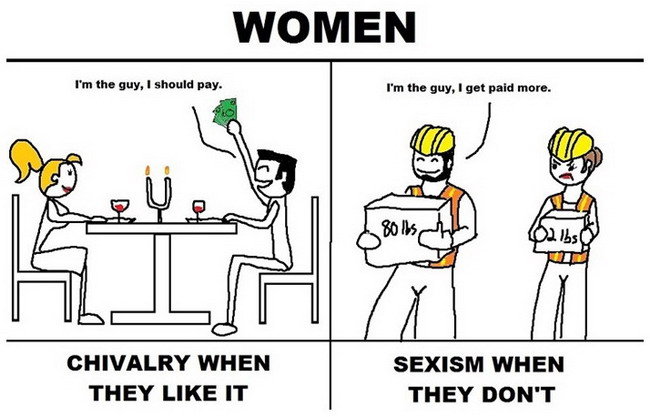
Don't always assume BOY prefer BLUE
GIRL prefer PINK
Sex-role stereotyping
- The assumption that certain roles or professions belong to Men and others belong to Women.
Suggestion to avoid sexism
-Avoid confirming and disconfirming to statement because of gender.
3) Heterosexism
- Having bias towards gays and lesbians, persume all people are heterosexual.
Suggestion to avoid heterosexism
- Avoid "complimenting" gay and lesbians on their heterosexual appearance.
Ageism-
But...below 55 is welcomed!
Suggestion to avoid sexism
- Avoid putting off elderly
- Be patient with elderly
Cultural Identifier
- Using preferred terms in talking to members of different cultures;
language that is free of sexism, heterosexism, racism or ageism.
1) Races (Malay, Chinese, India)
2) Avoid using words :GAY, LESBIAN
3) Age: older person ( > 65yrs) : elderly / senior citizen)
4) Sex
Young male (< 17 yrs) : Boy
Young female (< 17 yrs) : Girl
(> 17yrs) MAN, WOMAN
Using Verbal Message Effectively
Verbal message can
1) Symbolize
reality (partially)
- Don't present reality, but symbolize reality
Therefore, you purchase the Prada handbag not because it is really good (reality)
but you believe people said it is good (symbol).
Your mindset is following what other people said - Intensional
orientation
Extensional orientation
You try to understand and know about something or a person before you make any judgement
Allness- describe the world in extreme terms that imply one knows all
2) Messages / languages express both
facts and inferences
-We must clear that an accurate message must be made up of facts instead of inference.
I hate bright colors (inferential statement)
I love red colors (factual statement)
3) Messages and languages can be
relatively static
Messages or words used are formed based on our judgement and perception, how often do we update our perception?
Static Evaluation
-retain evaluation despite changes in a person or thing?

Tom is a lazy boy. (Five years ago)
Five years later, you still perceive Tom is a lazy boy even though he is now becoming hardworking.
Is it Fair for him??!
4) Messages/ language can obscure
distinction
- Over generalize people or things, blurring the distinction between people, objects or events.
Indiscrimination
- Fail to distinguish similar but different things or people
Example: You can't differentiate which chocolate is belonged to which brand without looking the packaging.

Polarization
-Tend to look at the worlds in term of opposite and describe in extreme.
-Not allowing the possibility.
Example: If most of the Chinese follow the teaching of Buddhism, you perceived that ALL CHINESE follow the teaching of Buddhism.



No comments:
Post a Comment